Difference between revisions of "Building Ventilation"
Difference between revisions of "Building Ventilation"
(→OWENS CORNING CANADA LP) |
|||
| (25 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| + | {{Template:RPM Info}} | ||
| − | < | + | {{DISPLAYTITLE:<span style="position: absolute; clip: rect(1px 1px 1px 1px); clip: rect(1px, 1px, 1px, 1px);">{{FULLPAGENAME}}</span>}} |
| + | __NOTOC__ | ||
| − | + | <big><big>Division E - General Information</big></big> | |
| − | + | <hr> | |
| + | <big><big><big><big><big>Building Ventilation</big></big></big></big></big> | ||
| + | {| class="wikitable" | style="color: black; background-color: #ffffcc; width: 100%;" | ||
| + | | colspan="2" | '''NOTICE TO READER''': This is an <u>information page only</u>. To read the standards applicable to a particular Waterproofing or Water-shedding System, refer to the actual Standard located in [[Division B | '''Division B''']]. | ||
| + | |} | ||
| − | + | <big><big><big>General</big></big></big> | |
| − | + | This section of the RCABC '''''Roofing Practices Manual''''' provides general information on the benefits, types of vents and BC Building Code Requirements for attic and roof space ventilation. The Reader is urged to consult all relevant codes governing construction design and practices in any given jurisdiction. | |
| − | + | <big><big><big>Benefits of Attic Ventilation</big></big></big> | |
| − | === | + | {| class="wikitable" style="vertical-align:top; margin-left:20pt; margin-right:auto; border:none;" |
| − | ; | + | |+ Attic Ventilation During Hot Weather |
| − | : | + | |- |
| − | ; | + | ! style="width:120px; text-align:centre;" | Unvented Attic |
| − | : | + | ! style="width:300px; text-align:centre;" | |
| − | ; | + | ! style="width:120px; text-align:centre;" | Vented Attic |
| − | + | |- | |
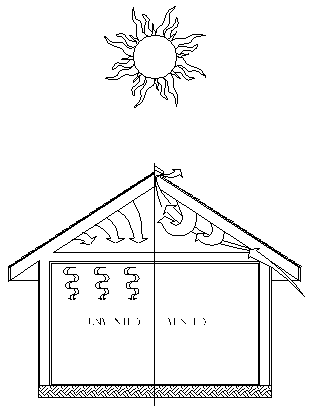
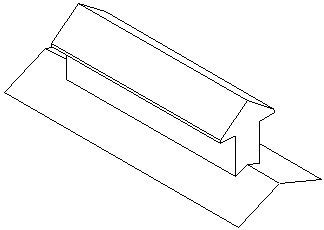
| − | ; | + | | Roof surfaces can reach temperatures in excess of 170° C. Radiant heat penetrates through roofing, increasing attic and living space temperatures. || [[File:Roofventhot.gif]] || Proper ventilation removes heat by causing air to move through the attic, keeping both the attic and living space cooler. |
| − | : | + | |- |
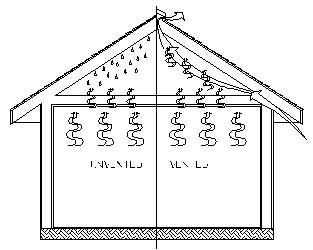
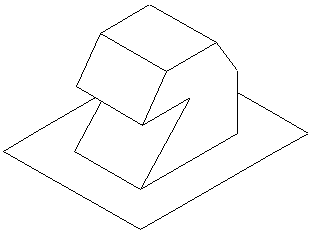
| + | | Moisture rising up through living space condenses in the attic, producing moisture on wood framing, insulation and roofing. || [[File:Roofventcold.gif]] || Proper ventilation allows moisture to escape as fresh, dry air moves through the attic. | ||
| + | |} | ||
| − | + | <big><big>Types of Pitched Roof Attic Vents</big></big> | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | ==== | + | <table border=0 cellpadding=3 cellspacing=0 width=500> |
| − | + | <tr> | |
| − | : | + | <th colspan=2>Natural Air Flow Ventilators</th> |
| − | + | </tr> | |
| − | : | + | <tr> |
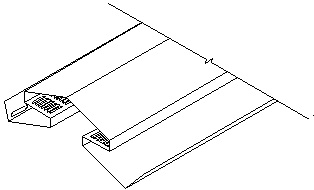
| − | + | <td><u>Plastic Continuous Ridge Air Vent</u></td> | |
| − | : | + | <td><u>Plastic Air Flow Vent</u></td> |
| − | + | </tr> | |
| − | + | <tr> | |
| − | ; | + | <td>[[File:Plasticridgevent.jpg]]</td> |
| − | + | <td>[[File:Plasticflowvent.jpg]]</td> | |
| − | + | </tr> | |
| − | + | <tr> | |
| + | <td colspan=2><u>Plastic Air Flow Vents</u><br><br>Acceptable plastic vents must conform to CSA - A93 -M82 (R 1992) or ICBO #4159. Vents must have a minimum 75 mm (3”) flange on the up-slope side and a minimum 50 mm (2”) flange on the remaining three sides. Continuous ridge air vents must provide a minimum of 50 mm (2”) of flashing flange to overlap roofing material on each side of the roof ridge. | ||
| + | </td> | ||
| + | </tr> | ||
| + | <tr> | ||
| + | <td>[[File:Metalridgevent.gif]]</td> | ||
| + | <td>[[File:Metalflowvent.gif]]</td> | ||
| + | </tr> | ||
| + | <tr> | ||
| + | <td colspan=2><u>Metal Air Flow Vents</u><br><br>Acceptable metal vents must have a minimum 100 mm (4”) flange to receive roofing on all sides and a minimum vertical sealed height of 75 mm (3”). All seams are to be fully soldered or welded. Galvanized steel must be a minimum of 26 gauge and aluminum must be a minimum of 20 gauge. Ridge vents must provide a minimum of 50 mm (2”) of flashing flange to overlap roofing material on each side of the roof ridge. | ||
| + | </td> | ||
| + | </tr> | ||
| + | </table> | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | <big><big>Attic and Roof Space Ventilation</big></big> | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | Requirements for Residential and Small Buildings (BC Building Code Section 9.19) | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | ==== | + | {| class="wikitable" style="vertical-align:top; margin-left: 20pt; margin-right: auto; border: none;" |
| − | ; | + | |+ Ridge, Soffit and Gable Ventilation |
| − | + | |- | |
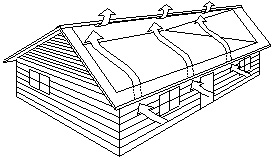
| − | ; | + | ! style="width:500px;"| Continuous Ridge Vent and Soffit Ventilation |
| − | : | + | ! style="width:500px;"| Gable End Vents and Soffit Ventilation |
| − | ; | + | |- |
| − | : | + | | style="text-align:center;" | [[File:ContinuousRidgeandSoffit.jpg]] || style="text-align:center;" | [[File:GableEndVentsandSoffit.jpg]] |
| + | |- | ||
| + | | style="text-align:left;" | Where insulation is installed between ceilings and the underside of roof sheathing, space shall be provided between the insulation and roof sheathing, and vents shall be installed to permit the transfer of moisture from the space to the exterior. (See Section 9.19 BC Building Code) Vents shall be in conformance with CAN3-A93 natural ventilators for buildings and shall be designed to prevent the entry of rain, snow and insects. || Ceiling insulation shall not be installed in a manner that will restrict free flow of air though roof vents or through any portion of the attic or roof space. The unobstructed vent shall be not less than 1/300 of the insulated ceiling area. On roofs sloped less than 1:6 (2” in 12”), that are constructed with roof joists, the vent shall not be less than 1/150 of the insulated ceiling area. | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | ! style="width:500px;"| Cathedral Ceiling | ||
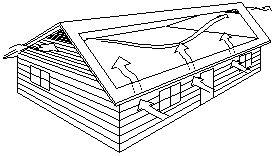
| + | ! style="width:500px;"| Roof Air Vents and Soffit Ventilation | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | style="text-align:center;" | Spaced Purlins provide air space || | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | style="text-align:center;" | [[File:CathedralCeiling.jpg]] || style="text-align:center;" | [[File:RoofAirVentsandSoffit.jpg]] | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | style="text-align:left;" | Where each joist space is not separately vented, roof joist spaces shall be interconnected by installing purlins not less than 38 mm (1 1/2 ”) by 38 mm (1 1/2 ”) on top of the roof joists. Not less than 63 mm (2 1/2 ”) of space shall be provided between the top of the insulation and the underside of the roof sheathing. || Vents may be roof, eave or gable end type or any combination thereof, as long as adequate ventilation is provided. The vents must be distributed uniformly on opposite sides of the building. Not less than 25% of required vent openings shall be located at the top of the attic or roof space, and not less than 25% of the required openings shall be located at the bottom of the space. The lower portion of the mansard or gambrel style roofs does not need to be ventilated. The upper portion requires ventilation as noted above. | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |} | ||
| − | + | </div><!-- mainBodyDiv --> | |
| − | + | </div><!-- row --> | |
| − | + | <div class="col-md-12"> | |
| − | + | <hr> | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | = | + | [[Main Page | <i class="fa fa-home fa"></i> Home]] |
| + | </div> | ||
| − | + | {{Tempate:RPM Page Footer with Copyright and Current Date}} | |
| − | |||
| − | : | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
Latest revision as of 15:33, 9 September 2021
Division E - General Information
Building Ventilation
| NOTICE TO READER: This is an information page only. To read the standards applicable to a particular Waterproofing or Water-shedding System, refer to the actual Standard located in Division B. |
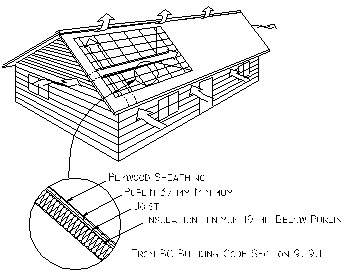
General
This section of the RCABC Roofing Practices Manual provides general information on the benefits, types of vents and BC Building Code Requirements for attic and roof space ventilation. The Reader is urged to consult all relevant codes governing construction design and practices in any given jurisdiction.
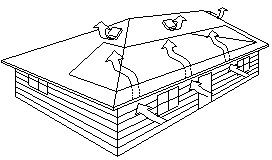
Benefits of Attic Ventilation
Types of Pitched Roof Attic Vents
Attic and Roof Space Ventilation
Requirements for Residential and Small Buildings (BC Building Code Section 9.19)
© RCABC 2024
No reproduction of this material, in whole or in part, is lawful without the expressed permission of the RCABC Guarantee Corp.