Template:Part 8 (Waterproofing Roofs - SBS)
Template:Part 8 (Waterproofing Roofs - SBS)
1 General
- Insulation overlay boards are installed in most conventionally insulated roof assemblies to
- protect heat-sensitive insulation materials from damage by heat and flame.
- protect insulation materials from accidental impact.
- provide dimensional stability to the roof system.
- distribute dead loads from heavy overburdens or equipment installed on top of the finished roof assembly.
- ensure the membrane performs as it should.
- provide a suitable substrate for membrane application.
- Insulation overlay boards may be mechanically attached or adhered, depending upon the insulation type and the design requirements of the roof assembly as a whole. See more information on Insulation Joints and Overlays in Essential Elements.
1.1 Design
1.1.1 RoofStar 15-Year Guarantee
- An insulation overlay is required for all insulated systems, regardless of the insulation type, and overlays must
- be at least 6.4 mm (1/4”) thick.
- possess a compressive strength of at least 690 kPa (100 psi).
1.1.2 All Projects
- An insulation overlay of one or more layers is required over all board-type insulation when
- the compressive strength of the insulation is less than 110 KPa (20 psi).
- the membrane will be applied with a torch flame, adhesives or hot bitumen.
- When heat-sensitive insulation materials are used in a roof assembly, they must be covered with a heat-resistant insulation at least 50 mm (2”) thick. This requirement does not apply to crickets manufactured from heat-sensitive insulation and installed above the insulation assembly or on an uninsulated supporting deck structure, since the crickets serve only to promote drainage. However, a minimum overlay of flat board heat-resistant insulation measuring at least 50 mm (2”) thick is strongly recommended. See also 7.1.2 Design.
- When torch-applied or hot-mopped membranes are specified for installation above crickets made from heat-sensitive insulation, the crickets must be protected from heat damage with insulation overlays. See also 8.3 Application.
- While minimum insulation panel thicknesses are permissible for some designs, the Design Authority may consider the constructability of the roof system from a material handling perspective. Therefore, when material are by their nature breakable, the specifier should consider specifying a thicker panel.
- A conventionally insulated roof assembly supporting an overburden must be designed with at least one layer of adhered composite insulation overlay
- no less than 12.7 mm (½") thick.
- with a minimum compressive strength of 620 kPa (90 psi).
See also 14.1.2.1 General
2 Materials
See Insulation Overlays accepted for use in RoofStar Guaranteed roof systems.
Table 8.1 Insulation Overlay Minimum Thicknesses Material Minimum Thickness - mm (in.) Asphaltic core board 4. 8 (3/16") Moisture-resistant gypsum core board 6.4 (1/4") High-density Insulation Board 12.7 (1/2") Composite and Laminated Overlay Board 6.4 (1/4") Fibreboard As listed in this Manual Membrane-laminated overlays As listed in this Manual Mineral wool As listed in this Manual
- Regardless of the type of insulation overlay, the overall thickness of insulation overlay boards shall not exceed 50 mm (2”). Minimum allowable thicknesses are shown in Table 8.1 above.
- Asphalt or paraffin-impregnated coated fibreboard roof insulation adhered with hot asphalt or an asphalt-based adhesive must be asphalt-coated on the top and bottom surface (minimum coated two-sides).
- Fire guard tape must be 150 mm (6”) wide
- self-adhering modified bituminous tape acceptable to the membrane manufacturer.
- Type IV fibreglass felt or No. 15 organic felt, applied with hot bitumen or cold adhesive.
3 Application
3.1 General
3.1.1 RoofStar 15-Year Guarantee
- See the requirements for a RoofStar 15-Year Guarantee in 8.1.1.1.
3.1.2 All Projects
- An insulation overlay of one or more layers is required over all board-type insulation when
- the compressive strength of the insulation is less than 110 KPa (20 psi).
- the membrane will be applied with a torch flame or hot bitumen.
- Heat-sensitive insulation and crickets must be protected from exposure to torch flame or hot bitumen with overlay panels. This may be accomplished with
- one layer of panels,
- at least 12.5 mm (1/2”) thick.
- offset from insulation joints by at least 300 mm (12”).
- continuously sealed with a flame-impervious tape along all joints with adjacent panels|| 2020-July-3 }}.
- two layers of panels,
- each at least 4.8 mm (3/16”) thick.
- offset from each other, from the adjacent layer, and from insulation joints by at least 300 mm (12”)
- one layer of panels,
- When multiple layers of an overlay board are specified, the joints between boards must be offset/staggered at least 300 mm (12") from adjacent layers and rows. See Figure 8.1. See also 7 INSULATION .
Figure 8.1 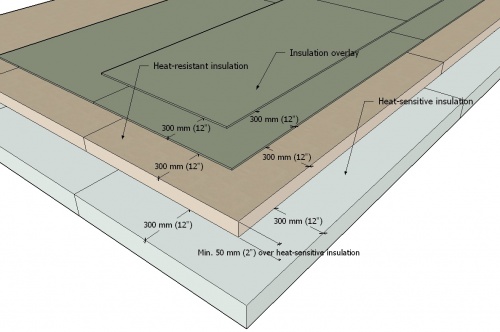
- When mechanically attaching insulation overlay boards, the insulation and overlay boards may be fastened together as one assembly. Unless otherwise indicated by the system requirements in a Tested Assembly, follow the fastener patterns set out in 3 SECURING the ROOF ASSEMBLY.
- When a composite overlay with an integrated base membrane is mechanically fastened over insulation, fasteners and plates used in the field of each panel must be covered with torch-applied polyester or composite-reinforced membrane patches that extend past the edge of each plate at least 50 mm (2”).
- Insulation in a conventionally insulated roof assembly supporting an Overburden must be overlaid with at least one layer of adhered composite insulation overlay
- at least 12.7 mm (½") thick.
- with a minimum compressive strength of 620 kPa (90 psi).
See 14 The ROOF as a PLATFORM for design and construction standards.
- Fibreboard shall not be used with torch-applied membranes.
- An insulation overlay is not required when the base layer of the primary roof membrane is mechanically attached, provided the insulation is heat-resistant and has a compressive strength of 110 Kpa (20 psi).
3.2 Overlaying Heat-resistant Insulation
- An insulation overlay is not required over heat-resistant insulation
- unless the
- compressive strength of the top layer of insulation is less than 110 KPa (20 psi).
- insulation is mineral wool and is mechanically fastened through the uppermost insulation layer.
- when the top layer in a multi-layered insulation assembly is adhered bitumen-faced mineral wool insulation.
- unless the
- When an overlay board is required over mineral wool insulation, the overlay board must be a moisture resistant gypsum core board measuring at least 12.7 mm (1/2") thick. See also 7.2 concerning Mineral Wool Insulation.
- A single layer of insulation overlay is acceptable when an overlay is specified for heat resistant insulation.
3.3 Overlaying Heat-sensitive Insulation
- When the roof membrane is applied with heat or hot bitumen, heat-sensitive insulation in the primary thermal assembly must be overlaid with a layer of heat-resistant insulation at least 50 mm (2”) thick. See 7.1.2.2(5) and 8.3.2 above.
- When EPS crickets are specified and installed, a minimum overlay of flat board heat-resistant insulation measuring at least 50 mm (2”) thick is strongly recommended. See also 7.1.2.2(9).
